Geostationary Satellite Breaks Down Geographical Barriers in Ultra-Remote Robotic Hepatectomy
Published 26 June, 2025
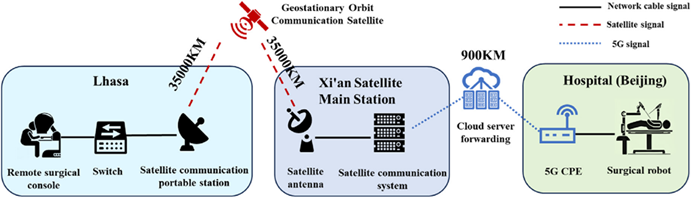
Healthcare inequality is a global challenge, with remote areas such as highlands and oceans lacking high-speed networks and specialized surgeons, making complex surgeries inaccessible. Conventional 5G telesurgery has a limited coverage radius (5,000 km) and relies on ground-based infrastructure. While satellite communication achieves global coverage (one satellite covers 1/3 of Earth’s surface), its 36,000-km altitude induces transmission latency exceeding 600 ms, far surpassing the surgical safety threshold (200 ms). Hence, achieving submillimeter precision under high latency is a major limitation for satellite-enabled telesurgery.
To that end, Prof. Rong Liu’s team from PLA General Hospital, collaborating with Northwestern Polytechnical University and Shanghai MicroPort MedBot, established a Lhasa-Beijing cross-regional link via the Asia-Pacific 6D high-throughput satellite. They implemented three key innovations:
- Adaptive Latency Compensation System: Integrating delayed-error synchronization with real-time neural network prediction to stabilize robotic arm error at 0.32±0.07 mm under 632 ms latency (conventional methods exceeded 2 mm error);
- Dual-Link Redundancy with Hot Switching: Backup 5G link activation within 280 ms upon satellite failure, with robotic arms autonomously entering position-hold mode;
- Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation: Prioritized transmission of surgical commands and critical imaging, enabling 1080P video transfer at 7.2 Mbps (62% bandwidth savings vs. traditional full-view transmission).
Two patients, a 68-year-old male with liver cancer and a 56-year-old male with hepatic hemangioma, underwent successful surgeries:
- Duration: 105–124 min; Blood loss: 20 mL;
- Satellite latency: 632 ms; Data loss rate: 2.8%;
- Discharge within 24 hours; Complications: Clavien-Dindo Grade I (minimal).
Prof. Liu emphasized: "This technology expands a single surgical robot’s service radius from 5G’s 5,000 km to satellites’ 150,000 km. In disaster medicine scenarios—this is critical for battlefield and earthquake rescue operations."
Funder: This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2021ZD0113301) and Beijing AI þ Health Collaborative Innovation Cultivation (Z221100003522005)...
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Article title: Feasibility and safety evaluation of remote robotic surgery under high latency conditions based on satellite communication, Intelligent Surgery, 10.1016/j.isurg.2025.05.001