A new one-step, green and economical way to prepare layered double hydroxides
Published 18 November, 2022
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) have a unique structure and many benefits, which have led to them being widely used in fields such as catalysis, environmental management and medical applications. Typically, soluble metal salts, such as metal nitrates, are used as the starting materials for the synthesis of LDHs, but they are relatively expensive and can be inconvenient to store and transport due to their explosive nature.
In a study published in the journal Magnetic Resonance Letters, a group of researchers from China outline a new synthesis approach they have developed – a one-step preparation route for layered double hydroxides that uses basic magnesium carbonate.
According to Luming Peng, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Nanjing University who led the team, this new process is not only cheaper than existing options, it also offers the potential to scale up production. He explains: “Basic magnesium carbonate is a common mineral in geology and planetology. It is inexpensive and available in large quantities, which makes it a perfect option for large-scale preparation of LDHs.”
The team found that when they added sodium hydroxide solution to a mixture of Al3+ solution with basic magnesium carbonate, magnesium (Mg)- and aluminum (Al)=containing LDHs formed rapidly at room temperature, possibly via a dissolution-recrystallisation mechanism.
Prof. Peng says: “The as-prepared LDHs are associated with nanosheet morphology and rich defects, while LDHs with high crystallinity and few defects can be obtained with high temperature hydrothermal treatment.”
He adds: “Our study is an innovation in the field of LDH synthesis. We believe it offers a promising route for further research and hope it will support production of less expensive LDHs for more applications in the near future."
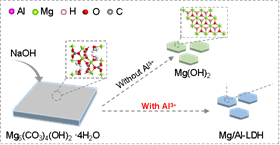
Image: The schematic representation of the conversion to Mg/Al-LDH from Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O. Credit: Luming Peng.
###
Contact the corresponding author: Luming Peng, luming@nju.edu.cn

